
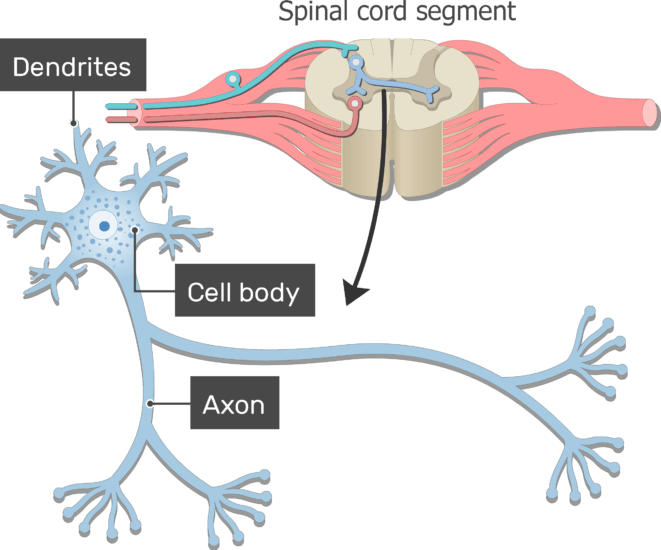
That suggests it is made of two organs-and you may not even think of the spinal cord as an organ-but the nervous system is a very complex structure. The picture you have in your mind of the nervous system probably includes the brain, the nervous tissue contained within the cranium, and the spinal cord, the extension of nervous tissue within the vertebral column. List the basic functions of the nervous system.Relate the functional and structural differences between gray matter and white matter structures of the nervous system to the structure of neurons.Identify the anatomical and functional divisions of the nervous system.Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous Systemīy the end of this section, you will be able to: But before you learn about that, you will see a big picture of the system-actually, a few big pictures. The focus of this chapter is on nervous (neural) tissue, both its structure and its function. In other chapters, the finer details of the nervous system will be explained, but first looking at an overview of the system will allow you to begin to understand how its parts work together. One easy way to begin to understand the structure of the nervous system is to start with the large divisions and work through to a more in-depth understanding. But our current level of understanding is probably nowhere close to that limit. It is an interesting conundrum to consider that the complexity of the nervous system may be too complex for it (that is, for us) to completely unravel. That quote is from the early 1990s in the two decades since, progress has continued at an amazing rate within the scientific disciplines of neuroscience. Kramer’s book Listening to Prozac, a pharmaceutical researcher is quoted as saying, “If the human brain were simple enough for us to understand, we would be too simple to understand it” (1994). The nervous system is a very complex organ system. Categorize the major neurotransmitters by chemical type and effect.Explain the differences between types of graded potentials.Describe the changes that occur to the membrane that result in the action potential.Describe the components of the membrane that establish the resting membrane potential.Distinguish the major functions of the nervous system: sensation, integration, and response.List the types of glial cells and assign each to the proper division of the nervous system, along with their function(s).Name the parts of the multipolar neuron in order of polarity.Describe the functional and structural differences between gray matter and white matter structures.Name the major divisions of the nervous system, both anatomical and functional.After studying this chapter, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
